Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Carbs and Energy Levels: Simple carbs provide quick energy, while complex carbs offer a sustained release, making them ideal for different energy needs.
- Blood Sugar Stability and Digestion: Complex carbs are digested more slowly, leading to steady blood sugar levels, which helps prevent energy crashes.
- Balanced Nutrition for Health Goals: A mix of simple and complex carbs can support various health goals, from workout energy to daily sustained energy.
At ALOHA, we believe eating healthy should be simple, satisfying, and genuinely good for you. That’s why we’re proud to offer plant-based, organic, and non-GMO nutrition that aligns with your wellness goals and makes healthy choices easier.
When it comes to energy, not all carbs are created equal. Some carbohydrates provide lasting fuel, while others can lead to an energy crash. The difference between simple and complex carbs plays a major role in how they impact our bodies and how we feel.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between simple and complex carbohydrates, highlight their unique benefits, and offer guidance on choosing the right carbs to keep you energized and balanced throughout your day.
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates, often shortened to “carbs,” are one of the body’s main energy sources, working alongside protein and fat to keep us going. When we eat carbs, they break down into glucose, which fuels everything from our muscles to our brains. Carbs power our bodies in ways that protein and fat can’t, providing the quick and efficient energy needed for daily activities and exercise.
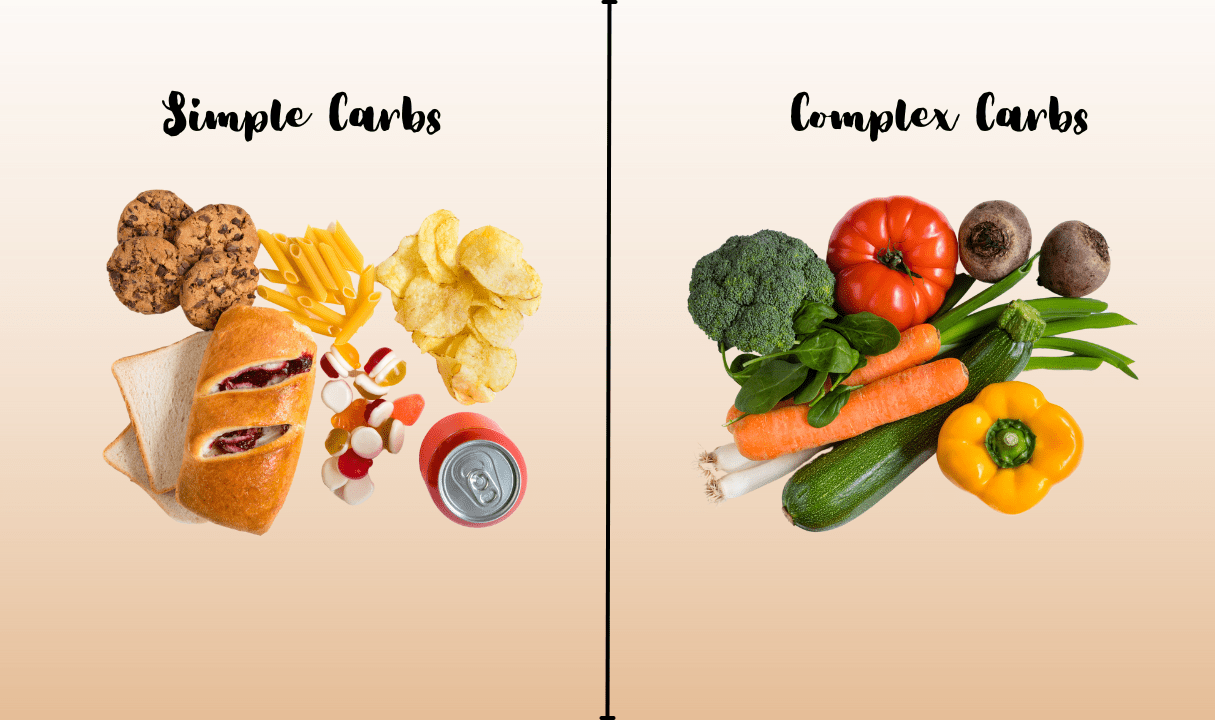
Carbs come in two main types: simple and complex. Simple carbs digest quickly, offering a fast boost of energy, while complex carbs break down more gradually, providing sustained energy over a longer period. Knowing how each type affects the body can help us make choices that fit our goals, whether keeping energy levels steady throughout a busy day or getting an extra lift during a workout.
Defining Simple Carbs: Quick Energy Sources
Simple carbs are carbohydrates made up of one or two sugar molecules, which makes them easy for the body to digest and absorb. This quick breakdown gives us an immediate burst of energy, which can be helpful when we need a fast pick-me-up, like before a workout or during a busy afternoon. You’ll often find simple carbs in foods like fruits, milk, sweeteners, and processed foods containing added sugars.
While simple carbs are great for short-term energy, they don’t provide the lasting fuel that complex carbs do. This is because the fast absorption of sugars can lead to a quick rise in blood sugar, followed by an equally quick drop—often called a "sugar crash." That’s why simple carbs are best enjoyed in moderation and paired with other nutrients that slow down digestion, helping to keep energy levels more stable.
Understanding Complex Carbs: Sustained Energy And Nutritional Value
Complex carbohydrates are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules, which means they take more time to break down in the body. This slower digestion process provides a steady, sustained release of energy, making complex carbs ideal for keeping energy levels balanced throughout the day. Foods rich in complex carbohydrates—like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes—often come with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that add extra nutritional value to your meals.
Because they digest more slowly, complex carbs help prevent the rapid blood sugar spikes and crashes associated with simple carbs. This makes them a great choice for fueling extended activities, supporting digestion, and maintaining a feeling of fullness. Including complex carbs in your diet can be a simple, effective way to get lasting energy while benefiting from the added nutrients supporting overall wellness.
Key Differences Between Simple and Complex Carbs
Understanding the differences between simple and complex carbs can help you make choices that align with your energy and wellness needs. Each type of carb has its digestion process, impact on blood sugar, and role in a balanced diet. Here’s a closer look at what sets them apart:
1. Digestion And Absorption Speed
Simple carbs are digested and absorbed quickly by the body because they contain one or two sugar molecules. This fast absorption provides a quick energy boost, which is useful when immediate energy is needed. However, the rapid rise in blood sugar levels can also lead to a sudden drop, leaving you tired or sluggish.
In contrast, complex carbs take longer to digest due to their longer sugar chains, which the body breaks down more gradually. This slower process leads to a steady release of glucose, keeping energy levels stable over time. As a result, complex carbs are ideal for prolonged activities or situations where sustained energy is beneficial.
2. Blood Sugar Impact
Due to their rapid digestion and absorption, simple carbohydrates cause a quick rise in blood sugar. This sudden spike is often followed by a sharp decline, resulting in what’s commonly known as a “sugar crash.” This quick drop can be disruptive for people looking to maintain stable energy and mood.
Complex carbs have a gentler effect on blood sugar, releasing glucose into the bloodstream at a slower pace. This steadier release helps to prevent sudden spikes and crashes, supporting balanced energy levels and reducing cravings. Complex carbs offer a more reliable choice for those seeking stable energy.
3. Nutritional Content And Satiety
Simple carbs, especially those found in processed foods and added sugars, often lack fiber and essential nutrients. While they provide quick energy, they don’t offer the same fullness or nutritional benefits as more complex options. This lack of fiber can also mean hunger returns quickly after consuming simple carbs.
Complex carbs, on the other hand, are often packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that provide additional nutritional benefits. Fiber not only aids digestion but also promotes a feeling of fullness, making complex carbs more satisfying. Foods rich in complex carbs, like whole grains and vegetables, can support digestive health and keep you energized for longer.
Health Benefits Of Simple Carbs And When To Consume Them
While simple carbs sometimes have a bad reputation, they can play a valuable role in your diet, especially when consumed correctly. Simple carbs provide quick energy, making them beneficial for certain situations where you need a fast boost. Here’s how simple carbs can support your energy and when they’re best enjoyed:
Quick Energy Boost for Physical Activity
Simple carbs are ideal when you need immediate energy, such as before or during high-intensity workouts. Because they’re digested quickly, they can provide a fast source of fuel that’s easy for the body to access. Athletes or anyone engaging in intense exercise can benefit from simple carbs to help power through a workout.
Supporting Blood Sugar In Low-Energy Moments
Sometimes, we need a quick lift to stabilize blood sugar, like during a long day or after an afternoon energy dip. Simple carbs can help raise blood sugar quickly, which is useful if you’re feeling low on energy or need a rapid pick-me-up. This quick response can be helpful for short-term energy needs.
Pairing With Other Nutrients For Balanced Intake
When eaten alongside protein, fiber, or healthy fats, simple carbs can be part of a balanced snack that’s easy to digest but keeps you fuller for longer. The added nutrients help slow down digestion, giving you the immediate energy of simple carbs without the rapid drop in blood sugar. This pairing can be beneficial if you’re looking for a quick but satisfying snack.
Health Benefits Of Complex Carbs And Ideal Consumption Times
Complex carbs offer more than just energy—they provide a range of benefits that support long-term health and wellness. Their slower digestion and higher fiber content make them ideal for sustained energy, blood sugar balance, and nutritional value. Here’s why complex carbs are a vital part of a balanced diet and when they’re most beneficial:
Sustained Energy Throughout The Day
Complex carbs are digested more slowly, providing a steady stream of glucose that keeps energy levels balanced. This makes them a great choice for meals that sustain you over several hours, like breakfast or lunch. Pairing complex carbs with ALOHA protein drinks can further enhance energy stability by providing additional plant-based protein, helping you stay productive without the energy crashes associated with quick-digesting foods.
Supporting Blood Sugar Balance
The gradual digestion of complex carbohydrates helps prevent sudden spikes and drops in blood sugar, making them ideal for stable energy and mood. This is especially helpful for people looking to avoid the “crash” often associated with simpler carbs. Consuming complex carbohydrates at regular intervals can contribute to smoother energy levels and better overall mood.
Promoting Fullness And Digestive Health
Complex carbs are often high in fiber, which helps with digestion and keeps you feeling fuller for longer. Fiber not only aids in digestive health but also slows down the absorption of sugars, promoting steady blood sugar levels. Incorporating complex carbs like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables into meals can help with satiety, supporting healthy eating patterns throughout the day.
Choosing The Right Carbs For Your Health Goals
Choosing between simple and complex carbs doesn’t have to be complicated. The key is understanding how each type of carb fits into your goals and when they can best support your energy and wellness. Here’s how you can make carb choices that work for your unique lifestyle:
For Quick Energy Needs
Simple carbs can be a great go-to if you need immediate energy—whether for a workout, a busy morning, or a sudden dip. They digest quickly, providing a fast fuel source when you need it most. Foods like fruit, honey, or a small smoothie can deliver the quick carbs you need to get through an active moment.
For Balanced, Lasting Energy
Complex carbohydrates are a smart choice when you want energy that lasts throughout the day. Including them in meals like breakfast or lunch can set a foundation of steady energy without spikes or crashes. Whole grains, vegetables, and legumes are examples of complex carbohydrates that support long-term stamina and balance.
Finding A Balance With Mixed Meals
Combining simple and complex carbs in the same meal can offer a balanced energy boost supporting short-term and sustained needs. Pairing fruit (a source of simple carbs) with oatmeal (a source of complex carbs) or adding a side of whole-grain bread to a quick smoothie can be a great way to combine benefits. This approach helps keep energy steady and makes meals more satisfying.
Final Thoughts
Carbohydrates are a fundamental part of our diet, influencing energy, mood, and overall wellness. Understanding the differences between simple and complex carbohydrates helps us make choices that support both immediate and sustained energy needs. Simple carbohydrates offer quick energy for those moments when we need an immediate boost, while complex carbohydrates provide long-lasting fuel that benefits digestion and balances blood sugar.
Incorporating a balance of simple and complex carbs allows for a flexible approach to eating that adapts to various lifestyle demands. Recognizing how each carbohydrate affects the body can empower us to align our food choices with our health goals, ensuring that we feel energized, focused, and nourished throughout the day. This awareness is a valuable tool in building a diet that meets our energy needs and supports long-term well-being.
Read also:
- How To Make A Protein Shake: Delicious Recipes And Tips
- Protein Powder vs. Protein Shake: Understanding The Differences
- Is Lactose-Free The Same As Dairy-Free?
Frequently Asked Questions About Simple Carbs Vs. Complex Carbs
What are some examples of simple carbs?
Simple carbs include fruits, dairy products, table sugar, and sweetened beverages. These foods provide quick energy but often lack fiber and other nutrients.
Where can you find complex carbs in foods?
Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and starchy foods like potatoes are abundant sources of complex carbohydrates. These provide longer-lasting energy and valuable nutrients.
How do simple carbs affect blood sugar levels?
Simple carbs cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, leading to a quick burst of energy. However, this is often followed by a drop, sometimes called a "sugar crash."
Why are complex carbs considered healthier for sustained energy?
Complex carbs digest slowly, offering a steady energy release, which helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevents sudden crashes in energy.
Are all simple carbs unhealthy?
Not all simple carbs are unhealthy; natural sources like fruits and dairy provide essential nutrients. The key is to avoid excessive processed sugars and focus on whole food sources.
How can you balance simple and complex carbs in your diet?
Pairing simple carbs with complex carbs or fiber-rich foods can prevent blood sugar spikes. For example, combining fruit (simple carb) with oats (complex carb) provides balanced energy.
What role does fiber play in complex carbs?
Fiber in complex carbs aids digestion, promotes fullness, and slows sugar absorption. This helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports a healthy digestive system.
Can simple carbs be beneficial for athletes?
Yes, simple carbs provide a quick energy boost, making them useful for athletes before or during intense workouts for fast fuel.
Do complex carbs help with weight management?
Complex carbs are high in fiber, which promotes fullness and reduces overeating. This can support weight management by keeping hunger levels balanced.
What are the main differences between simple and complex carbs?
Simple carbohydrates digest quickly, offering immediate energy, while complex carbohydrates, due to their slower digestion, provide sustained energy. When chosen thoughtfully, both can be part of a balanced diet.
Sources:
1. Holesh, J. E., Martin, A., & Aslam, S. (2023). Physiology, Carbohydrates. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459280/
2. Clemente-Suárez, V. J., Mielgo-Ayuso, J., Martín-Rodríguez, A., Ramos-Campo, D. J., Redondo-Flórez, L., & Tornero-Aguilera, J. F. (2022). The Burden of Carbohydrates in Health and Disease. Nutrients, 14(18), 3809.
3. Murray, B., & Rosenbloom, C. (2018). Fundamentals of glycogen metabolism for coaches and athletes. Nutrition Reviews, 76(4), 243–259. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuy001
4. Mul, J. D., Stanford, K. I., Hirshman, M. F., & Goodyear, L. J. (2015). Exercise and Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 135(135), 17–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.07.020
5. American Heart Association. (2018, April 16). Carbohydrates. Www.heart.org. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/carbohydrates
6. Cherney, K. (2023, May 10). Simple Carbohydrates vs. Complex Carbohydrates. Healthline; Healthline Media. https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/simple-carbohydrates-complex-carbohydrates
ALOHA's products are not intended to treat, diagnose, mitigate, prevent, or cure disease. ALOHA's products should not replace prescribed medications or the variety of foods important to a healthful diet.
Do not self-diagnose any health condition. Work with your healthcare provider to determine how best to achieve optimal health.